Currently, blockchain and cryptocurrency platforms are tackling several critical challenges. Among them, a major concern for established digital currencies is trending at the forefront of the agenda. is scalability Yet, blockchain interoperability introduces an altogether different framework for the digital landscape. Although scalability solutions are making headway, examining pioneering projects, advanced technologies, and the hurdles facing network interconnectivity is imperative.

From platforms revolutionizing as the bedrock of blockchain interaction to burgeoning open protocols, the capability for these networks to communicate heralds a transformative era for the digital world.
How Is It Going to Work?
Currently, interoperable technology comprises numerous dynamic elements; some are operational whereas others are still theoretical. Regardless, the innovations driving future connectivity are both captivating and industry-leading.
A challenge of connecting blockchain systems is their diverse 'languages'. These intricate systems vary in their smart contract abilities, transaction models, and consensus mechanisms. To tackle this, we need solutions that enable universal interactions akin to the early days of the web with open protocols.
While crypto interoperability solutions are complex, we can break them down into:
- Open Protocols
- Multi-Chain Frameworks
Open protocols act as a standardized medium helping blockchains to exchange data and value with one another. They serve as the digital communication framework and are the essence of the internet. Multi-chain frameworks provide diverse chains an open environment to connect under decentralized governance layers. These frameworks are generally more intricate than single protocols and are backed by prominent platforms with designated tokens.
Open Protocols
Atomic swaps, noted as a prominent open protocol, allow decentralized cross-chain transactions without third-party involvement. For example, directly trading 1 BTC for 1 ETH bypassing exchanges, emphasizing its inherent protocol function.

Read: What Are Atomic Swaps?
Interledger An advanced open-source atomic swap model, the Interledger protocol, is described as superior in functionality. It is modeled on the internet, involving layers that dictate communication flow between nodes.
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Interledger Layer
- Ledger Layer
Application Layer – This component manages initiator and recipient addresses and chooses transport methodologies.
Transport Layer – Functions as the connecting protocol mediating transaction conditions.
Interledger Layer – Ensures data transfer by coordinating standard addresses and flow via Interledger Protocol for node exchanges.
Ledger Layer – Determines the swap's settlement method, featuring an extensible plugin architecture.
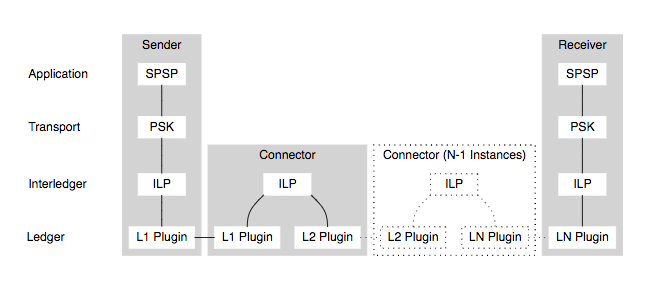
Image Credit – Courtesy of Interledger Protocol Website
Even including traditional finance systems like banks, Interledger facilitates integration.
Atomic swaps represent a practical open-source framework for blockchain interaction, potentially leading the way in cross-chain solutions versus larger, more intricate multi-chain frameworks.
Multi-Chain Frameworks
Environments conducive to value exchange across multiple blockchains encapsulate multi-chain frameworks, plugging diverse blockchains into a cohesive setup. Various platforms are shaping these ecosystems distinctly while staying within the central ideology.
These are often labeled as the 'Internet of Blockchains', offering innovative and promising capabilities.
Polkadot
Polkadot Operating seamlessly within Polkadot, parachains illustrate a sub-chain framework that allows significant scalability through characteristic diversity and transaction dispersion.
Polkadot distinguishes itself by focusing on not only transaction but data sharing, embodying smart contracts and applications, contributing to its ambitious complexity and unique potential.
Polkadot’s structure is divided into three levels:
- Relay Chain
- Parachain
- Bridges
The relay chain manages the network's consensus system, meaning all linked chains adopt Polkadot's Proof-of-Stake model.
Individual blockchains, or parachains, within Polkadot still retain the freedom to innovate their blockchain design, offering more flexibility compared to Ethereum.
Links or bridges allow integration to independent blockchains like Ethereum, requiring trust-based connections.
Polkadot is essentially a baseline protocol and structural framework benefiting blockchains by plugging them into a scalable network.
Cosmos
Cosmos Comparable to Polkadot, another framework emphasizes transaction-based integration over smart contracts. Notably, Cosmos does not strip blockchains of their consensus, forming a decentralized network powered by Tendermint .
Tendermint, a general-purpose blockchain engine with Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus, serves as Cosmos’s foundational framework. Cosmos comprises three layers:
- Bottom – Tendermint
- Middle – Cosmos Network of “Zones”
- Top – Cosmos “Hub”
Like Polkadot's zones, Cosmos offers standardized protocol benefits, maintaining sovereignty with a regulatory model either private or public in nature.
Cosmos Hub, paralleling Polkadot's Relay, unites the zones with a seamless, standardized interaction. Initially, it will be permissionlessly tied to Atom tokens, anticipating future independent hubs.
Beyond the technologies, an essential facet is ensuring developer collaboration within open-source projects. Platforms like Hyperledger offer conducive environments for developing blockchain systems.
Hyperledger Accentuating enterprise blockchain development, Hyperledger under the Linux Foundation should inspire the wider community. Their achievements and open-source collaboration hubs like Github could propel blockchain integration.
Use Cases
The intertwining of blockchain networks, through open protocols or multi-chain frameworks, is poised to usher in a new chapter for the industry, albeit alongside current scalability concerns.
Among numerous potential applications, the healthcare sector stands out as particularly impactful. Though advanced and innovative, it suffers from disjointed regulations and data management. permissioned or permissionless The advent of interoperable network solutions in varied health sectors could potentially revolutionize the field, although not imminent, healthcare is likely to be a pioneer in adopting blockchain integration.
Read: Ways Blockchain Technology Can Revolutionize Healthcare
The concept of decentralized identity shines brightly in contexts similar to that of healthcare, presenting unique opportunities. The multitude of government regulations coupled with various identification frameworks makes the task of issuing and verifying digital identities a complex affair. Furthermore, the prevalence of identity fraud due to the repetitive nature of digital submissions with third-party systems adds another layer of complication. Projects like Civic and identity attestation standards on platforms like Ethereum offer promising solutions currently in play. Still, if blockchain networks were interoperable, they could significantly streamline these processes across different types and jurisdictions of identity management.
Conclusion
The uncharted waters of emerging technologies, particularly blockchain, are both thrilling and unpredictable. While predicting the exact path ahead for blockchain remains challenging, we do have cutting-edge innovations and bold platforms providing insights and glimpses into the potential future of blockchain interoperability.





1Comment
You might be overlooking the most promising project tackling interoperability challenges, which is the Quant Network with its distinctive Overledger technology. It resolves interoperability issues without relying on a single ledger.