In the dynamic world of blockchain, Layer 3 systems have become a pivotal force by focusing on the creation and support of decentralized applications (DApps).
Orbs are not only an example of a Layer 3 blockchain network, Despite the rise of Layer 3, Orbs has gained significant recognition as a pioneering force in this realm. to coin this term .
Since its inception in 2017, more than 30 dedicated professionals, spread across cosmopolitan hubs like Tel Aviv, London, New York, Tokyo, and Seoul, have been nurturing its growth.
Immediate Insight: Orbs stands as a Layer 3 blockchain network dedicated to refining decentralized applications, offering an environment tailored to each app's governance and economic needs.
Quick Facts
| Category | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Concept of Layer 3 Networks | Strive to develop DApps that seamlessly integrate with Layer 1 blockchains, providing a tailor-made ecosystem for each application with customized rules, governance, and economic rewards, thereby enhancing their scalability and efficiency. |
| Orbs Network | Showcasing a Layer 3 blockchain example: it serves as a 'decentralized backend' enhancing smart contract abilities and acting as a serverless cloud for advanced L3 services. |
| Development and Team | Established in 2017 and guided by a team stationed in key cities around the globe including Tel Aviv, London, New York, Tokyo, and Seoul. |
| Interoperability and Privacy | Promotes seamless interactions between various decentralized apps, equipped with customized privacy attributes and encryption to cater to specific application requisites. |
| Orbs Offerings | Supports multi-chain staking across Ethereum and Polygon utilizing the Tetra Staking Wallet for smooth interaction, alongside ORBS tokens for staking and delegating. |
| Getting Started with Orbs | Hold ORBS tokens to engage in staking, then choose a Guardian for delegation with a requirement of a 14-day lock period once tokens are staked. |
| Staking with Tetra Wallet | Using MetaMask, connect and stake ORBS tokens, opt for a Guardian, and explore unstaking and withdrawal options. |
| Importance of Layer 3 Networks | Tackling scalability challenges in decentralized applications, Layer 3 networks offer an optimized environment facilitating complex smart contract functionalities and a thriving crypto environment. |
What Is Orbs?
Within the blockchain sphere, Layer 3 networks are seen as application-specific extensions built over existing Layer 1 blockchains, providing a unique operational space for each DApp to independently manage its own rules, governance, and economic motivations.
Conceptualized as a distinct decentralized execution tier, bridging between L1/L2 and the application layers, functioning as a 'decentralized backend' to elevate smart contracts and broaden the potential for Web 3.0, DeFi, NFTs, and GameFi.
When hosting a singular application, a Layer network can be finely tuned to cater to the application’s demands, promoting superior scalability and performance beyond the restrictions posed by running directly on a Layer 1 blockchain.
With Layer 3 networks like Orbs, there's a push towards interoperability, using established protocols and interfaces to ensure smooth communication and data exchange across decentralized applications, fostering a more interconnected ecosystem.
Orbs’ Infrastructure can be customized with privacy and encryption features tailored to the needs of each application, safeguarding sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access through network isolation.
Developers gain the ability to apply enhancements and distribute updates at an accelerated pace, experimenting with new features, tweaks, or governance schemes without disrupting the foundational Layer 1 blockchain.
As the complexities in DeFi and Web 3.0 solutions surge, and smart contracts meet their design limitations, the Orbs Network positions itself as a decentralized cloud service, empowering developers to integrate L3 services into smart contracts, sustained by Orbs PoS Guardians.
Integrating into a layered blockchain framework, Orbs brings enhanced capabilities to smart contracts, empowering solutions like dLIMIT, dTWAP, and Liquidity Hub.
What Does Orbs Offer?
Multi-chain Staking
The latest iteration, Orbs PoS V3, employs a hybrid architecture to enable multi-chain PoS staking over Ethereum and Polygon, benefiting from Ethereum's secure base layer and Polygon's scalability and affordability as a secondary layer.
Orbs patrons can choose to stake on Ethereum or Polygon; each chain requires its native tokens for transaction fees, with ETH necessary for Ethereum, and MATIC for Polygon.

Tetra Staking Wallet
The Tetra wallet offers a streamlined interface for engaging with the staking contract, facilitating token staking and Guardian delegation.
Beyond facilitating seamless token staking for rewards, the wallet empowers community members to enhance network security and operation.
Though the staking wallet is free from transaction charges, users might incur gas or bridging fees when executing smart contracts on Ethereum and Polygon.
Accessible on both desktop and mobile (Android and iOS), the wallet integrates with platforms such as Metamask, Status Wallet, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet, and MyEtherWallet.
How to Get Started with Orbs?
To engage with the Orbs ecosystem, possessing ORBS tokens is essential for staking and delegating voting power to a Guardian, who symbolizes the Orbs community and their long-term ambitions.
Guardians, tasked with assembling a network of Delegators, hold the responsibility of authentically representing both their and the network's interests, urging Delegators to select vigilant and trustworthy Guardians while keeping tabs on their performance.
Reward distribution settings allow participants to allocate staking rewards between Guardians and their Delegators. The prevailing setup sees Guardians receiving a third of rewards, with Delegators obtaining two-thirds, translating to a reward rate of 10% for guardians and 6.67% for delegates.
In ensuring all PoS network participants remain committed to maintaining network security, Orbs enforces a 14-day lock period on tokens, ceasing both staking and rewards if a Delegator opts for withdrawal.
Step-by-step Guide to Staking ORBS and Delegating to a Guardian Using Tetra Wallet
Begin by confirming your MetaMask installation on your browser alongside the Tetra Wallet, which can be sourced from staking.orbs.network.
Upon setting up MetaMask, link it to TETRA, then proceed to copy or create a QR for your address.
To commence staking with a Guardian, click STAKE YOUR TOKENS, specify the stake amount, selecting an ETH fee for transaction broadcasting within MetaMask. After waiting for 7 confirmations, click PROCEED to pick a Guardian and finalize staking.
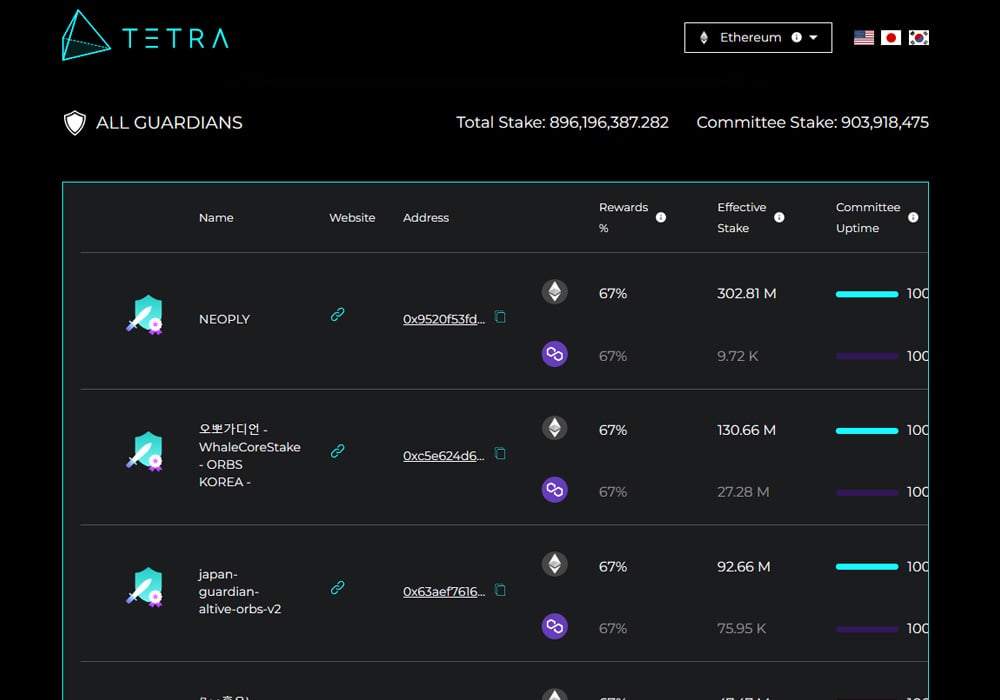
Post confirmation, advance to selecting a Guardian for staking, consult the gas fee in the browser window and allow MetaMask to process the transaction. Your tokens will then be successfully staked.
To retract your staked tokens, click UNSTAKE, define your preferred fee in the browser window, and authorize MetaMask to handle the transaction.
Should you choose to extract your ORBS, HIT WITHDRAW YOUR TOKENS in the dedicated withdrawal section.
For switching Guardians, select your preferred choice using the selector on the right, then enter the gas fee via MetaMask and allow time for transaction processing.
Understanding the Essential Role of Layer 3s in Blockchain Evolution
The advent of Layer 3 networks signifies a pivotal shift in confronting scalability, one of the foremost hurdles faced by decentralized apps.
While Layer 1 oversees multiple applications in tandem, Layer 3 networks are attuned to the demands of individual applications. This specificity fosters enhanced throughput and performance by concentrating on a single DApp, while facilitating greater smart contract and decentralized application complexity.
Synchronized with existing Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols, Orbs as a Layer 3 blockchain is designed to mitigate scalability constraints prevalent in Ethereum. By enabling smart contracts on L3 networks to process multiple trades or transactions, a more cohesive and interconnected crypto landscape is fostered.
Customizing each DApp's governance, rules, and incentives not only refines the user experience but also allows developers to craft intuitive interfaces specific to their apps, broadening accessibility and appeal.